Ultrasonic textile cutting is revolutionising the way we approach fabric and material processing. Using high-frequency vibrations, this advanced technology allows for precise and clean cuts, eliminating frayed edges and reducing waste. With our ultrasonic cutting solutions, we have seen significant improvements in speed and efficiency, benefiting a range of industries from textiles to electronics.

What sets ultrasonic cutting apart from traditional methods is its ability to cut and seal materials in a single step. This not only enhances productivity but also reduces the need for additional consumables. Whether we are working with woven fabrics or non-woven products, the precision and reliability of ultrasonic cutting are unmatched.
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, embracing innovations like ultrasonic textile cutting can provide a competitive edge. By streamlining production processes and enhancing product quality, we can meet the demands of modern industries more effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasonic cutting uses high-frequency vibrations for clean, precise cuts.
- It efficiently cuts and seals materials, reducing the need for extra consumables.
- This technology enhances productivity and quality in various industries.
What is Ultrasonic Textile Cutting?
Ultrasonic textile cutting involves using high-frequency vibrations to slice through fabrics with great precision. These vibrations cause a blade to oscillate rapidly, generating heat through friction.
This method melts the fibres right at the cutting line. As a result, the fabric edges are sealed immediately, avoiding fraying without needing additional steps.
Our approach to ultrasonic cutting is effective for various materials. We can cut through rubber, non-woven fabrics, and composite materials. Unlike traditional cutting methods, this technology offers clean cuts and reduced waste.
Additionally, our process can achieve impressive speeds. We can make up to 120 cuts per minute for smaller items such as textile labels. For continuous cutting, we can reach up to 25 metres per minute. This speed doesn’t compromise quality, as the edges remain neat.
Using ultrasonic cutting, we see several benefits:
- High Precision: Each cut is accurate and clean.
- No Consumables: We eliminate the need for adhesives or consumables.
- Efficiency: The process combines cutting and sealing, saving time.
- Versatility: Applicable to various fabric types and sizes.
In textile manufacturing, ultrasonic cutting has revolutionised how we achieve precision and efficiency. By incorporating this technology, we enhance productivity and deliver high-quality results.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Cutting over Traditional Methods
Clean and Fray-Free Edges: Ultrasonic cutting seals the fabric edges as it cuts, preventing fraying and unravelling. This results in a superior quality product with better aesthetics.
Reduced Heat Damage: Unlike laser cutting, which uses intense heat, ultrasonic cutting generates minimal heat. This means there is no scorching or burning of delicate fabrics, preserving their original texture and integrity.
Versatility Across Materials: Our ultrasonic cutting equipment can handle a variety of textiles. From synthetics like polyester and nylon to natural fibres like cotton and wool, it even handles layered and technical textiles with ease.
Reduced Operational Costs: Using ultrasonic cutting, we eliminate separate steps for fraying and sealing, saving significant time and labour. Additionally, ultrasonic blades have a longer lifespan compared to traditional blades, which reduces replacement costs.
Environmentally Friendly: This method is solvent-free, minimising environmental impact. Traditional methods often use glues or adhesives to seal edges, but ultrasonic cutting avoids these pollutants completely.
Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Textile Cutting
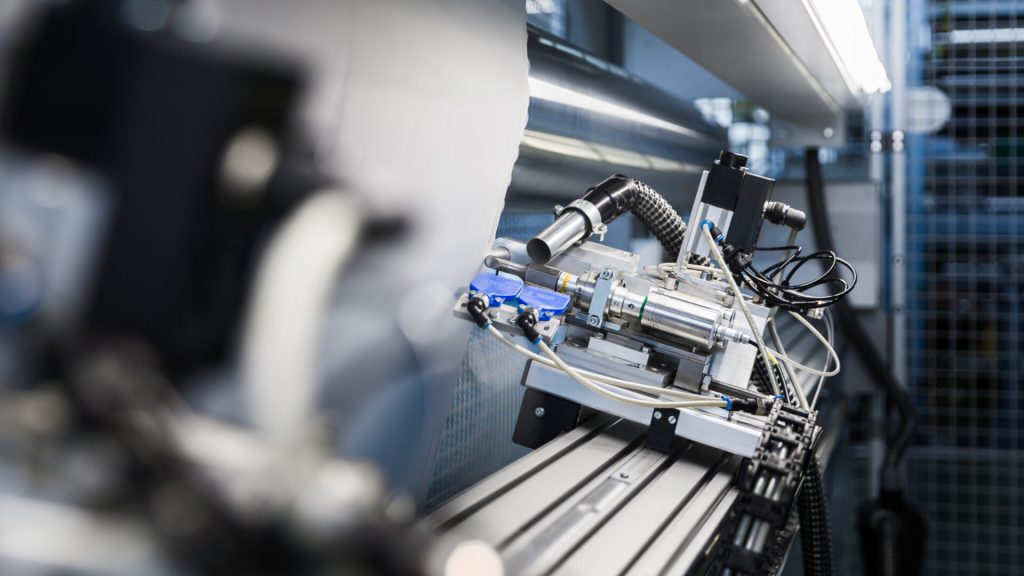

Ultrasonic textile cutting is an advanced technique that employs high-frequency sound waves to ensure precise cuts. This method is beneficial for achieving clean edges without fraying and increasing productivity in textile manufacturing.
Principles of Ultrasonic Cutting
Ultrasonic cutting operates on the principle of using high-frequency sound waves to create rapid vibrations. These vibrations, typically ranging from 20,000 to 35,000 vibrations per second (20kHz, 35kHz) generate heat through friction. This heat is concentrated on a cutting blade which effortlessly slices through the material. The cutter’s oscillation is so fast that it minimises material deformation and ensures a smooth and clean cut.
The cutter is driven by an ultrasonic generator, which converts electrical energy into ultrasonic frequency. This frequency is then transmitted to a booster, amplifying the vibrations before they reach the cutting blade, maximising the cutting efficiency. This process allows us to cut through various textiles, including both woven and non-woven materials.
Components of Ultrasonic Cutting Systems
An ultrasonic cutting system comprises several key components: the generator, booster, anvil, and cutter. The ultrasonic generator plays a crucial role, converting electrical energy into ultrasonic frequency vibrations.
The booster amplifies these vibrations’ intensity, making the cutting process more efficient. It is connected to the cutting blade, which oscillates at high frequency.
The anvil serves as a support surface where the cutting material is placed. It works in conjunction with the moving blade to accomplish precise cuts. The cutter itself is a blade that vibrates at high ultrasonic frequencies, slicing through materials with minimal effort.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Textile Cutting
Ultrasonic textile cutting offers several significant advantages. First, it provides high precision, making it suitable for intricate patterns and delicate fabrics. The ultrasonic frequency vibrations ensure extremely clean cuts, reducing fraying and giving a professional finish to the edges.
Furthermore, this method is highly productive, with speeds reaching up to 120 cuts per minute. The ability to cut and seal edges in one motion without additional consumables is another notable benefit, reducing operating costs.
The use of an ultrasonic cutter also means less manual effort is required, enhancing worker safety and reducing fatigue.
Textile Applications and Materials

Ultrasonic cutting is highly effective in various textile applications, offering precision and speed without fraying fabric edges. This section explores its role in different industries and the types of materials best suited for this technology.
Applications in Different Industries
Ultrasonic cutting is widely used in the textile industry for its efficiency and clean cuts. For instance, it is popular in apparel manufacturing. Here, the technology ensures precise cuts in woven fabrics, making it easier to produce intricate designs. The method also excels in cutting non-woven fabrics, which are commonly used in medical textiles such as gowns and masks.
In the automotive industry, ultrasonic cutting helps in creating interior components like seat covers and carpets. It can handle materials such as rubber and composite fabrics, ensuring durability and precision. Ultrasonic cutting is used widely in the tyre manufacturing industry.
This technology is also significant in the sportswear sector. It allows for the production of high-performance gear that requires accurate cuts and strong seams.
Materials Suited for Ultrasonic Cutting
Ultrasonic cutting works exceptionally well with a variety of materials. Woven fabrics, including cotton and polyester, benefit from the clean edges and speed of this process. By using high-frequency sound waves, we can achieve cuts that do not fray, enhancing the material’s durability.
Non-woven fabrics are also ideal for ultrasonic cutting. These materials, made from fibres bonded together, often present challenges for traditional cutting methods. Ultrasonics provide a solution by handling these fabrics with ease, making it perfect for applications where strength and precision are crucial.
Plastic and rubber materials also see significant benefits. In industries like automotive and medical, these materials require precise cutting and sealing, which ultrasonic technology offers.
For more information, you can visit RINCO’s ultrasonic cutting for textiles
Technical Aspects of Ultrasonic Cutting
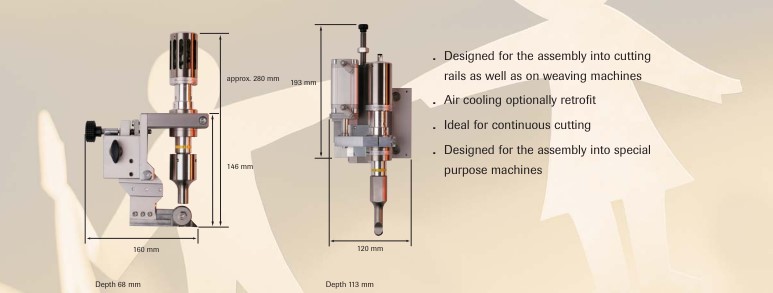
Ultrasonic cutting of textiles involves detailed precision and specific frequencies to achieve clean and fray-free edges. Here, we explore the technical aspects that make this process effective and efficient.
Optimising Cutting Precision
Precision is crucial in ultrasonic cutting, especially when dealing with textiles. The ultrasonic vibrations allow for sharp and accurate cuts or smooth edges without fraying. High-frequency vibrations produce heat during cutting, which melts and seals the edges.
We use special tools called sonotrodes and anvils. These tools conduct the ultrasonic energy to the material. They need to be precisely aligned to ensure consistent cuts.
Using CNC machines can further optimise precision. These machines can control the movement and pressure applied during the cutting process, ensuring uniformity and reducing waste.
Understanding Ultrasonic Frequencies
The frequency of ultrasonic waves plays a key role in the cutting process. Frequencies typically range from 20 kHz to 70 kHz depending on the textile material. Higher frequencies are typically used for thinner and more delicate fabrics, while lower frequencies are effective for thicker materials.
Correct frequency settings prevent damage to the material. Too high a frequency can lead to burning or melting, while too low can result in improper cutting. Selecting the appropriate frequency is essential for both productivity and quality.
We monitor frequencies closely using ultrasonic generators. These devices ensure the frequency remains stable throughout the cutting process, delivering consistent results. Using the right frequency also minimizes waste and optimizes production efficiency.
Manufacturing Processes
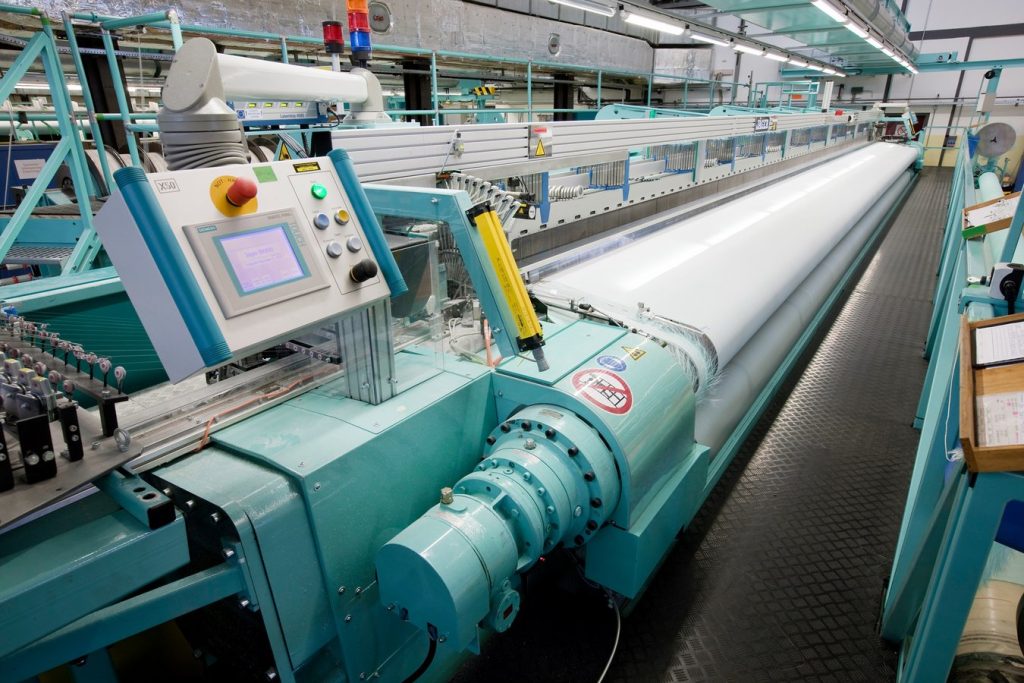

In this section, we look at how ultrasonic textile cutting works in manufacturing, including how it integrates with different manufacturing modules and its role in cauterisation and bonding.
Integration with Manufacturing Modules
Sabre Plastics Tooling can integrate Rinco Ultrasonic Cutting solutions onto any existing textile weaving machine.
Ultrasonic textile cutting is highly adaptable and can be integrated into various manufacturing modules with ease. This allows for automation, where machines can cut materials with precision and speed.
We often see ultrasonic cutters combined with roll-to-roll systems for continuous fabric processing. The process can be seamlessly added to existing production lines, improving efficiency with minimal downtime.
Key benefits include:
- Precision: Cuts are clean and accurate.
- Efficiency: Reduces manual labour needs.
- Compatibility: Works with many types of machines.
Ultrasonic systems can also be programmed to handle different fabrics, adjusting settings based on material properties. This makes the technology versatile for various textile applications.
Cauterisation and Bonding
Ultrasonic cutting does more than just slice through fabric. It also plays a crucial role in cauterisation, sealing the edges to prevent fraying. This is especially useful for materials like rubber, non-woven fabric, and composites.
The technique involves high-frequency vibrations that generate heat, causing the fabric to melt slightly at the cut edge. This forms a clean, sealed edge without additional finishing steps.
Additionally, ultrasonic cutting can bond layers of fabric together. This is vital in applications requiring strong, seamless joins. For instance, the continuous cutting with a Roll-Sonotrode can simultaneously cut and bond seams, enhancing productivity.
By integrating these capabilities, manufacturers achieve superior product quality and durability, all while streamlining their production processes.
Design and Functional Benefits
Ultrasonic textile cutting offers improved precision and cleaner edges compared to traditional methods. It reduces material waste and the need for additional processing steps.
Reduction of Fraying and Waste
One key advantage of ultrasonic cutting is its ability to cut through textiles without causing fraying. This is achieved through high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations that make clean, precise cuts. As a result, the edges of the textile are sealed during the cutting process, effectively eliminating fraying.
This sealing also contributes to reducing waste. By creating exact cuts, we can minimise excess material, leading to more efficient use of resources. This is especially important in industries dealing with costly fabrics where every inch counts.
Additionally, with the reduction of wasted material, we not only save on costs but also contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Alternative Solutions and Enhancements
Ultrasonic cutting provides advantages over traditional methods like manual cutting or rotary cutters. Unlike manual methods, ultrasonic cutting offers consistent precision, eliminating human error. Traditional methods often require additional finishing steps to handle fraying, but with ultrasonic cutting, this is not necessary.
Incorporating ultrasonic cutting with Industry 4.0 technology enhances its capabilities. For instance, automated systems can further increase efficiency and precision. Such integrations enable the combination of cutting and welding applications in a single step, sealing edges and reducing the need for separate processes.
This means critical materials like rubber, non-woven fabrics, and composite materials can be effectively managed, providing additional functional benefits over conventional methods.
Product-Specific Considerations
In this section, we focus on ultrasonic cutting applications tailored for various textile accessories and how to optimise processes for high-speed production. We discuss the practicalities and benefits of using ultrasonic technology in specific product contexts.
Ultrasonic Cutting for Textile Accessories
When it comes to textile accessories like belts, masks, and straps, precision is key. Ultrasonic cutting allows us to achieve clean edges without fraying. This ensures a neat, professional finish which is particularly important for visible accessories.
Bracelets made from fabric or composite materials also benefit from ultrasonic cutting. The method delivers exact cuts, maintaining the integrity of delicate designs. Additionally, ultrasonic cutting is suitable for products like nappies and towels, where hygiene and efficiency are essential. The clean cuts reduce waste and enhance the product’s durability.
We can achieve high-quality finishes on piping and rope, vital for both functionality and appearance. The ability to cut and seal in a single step saves time and resources, making the production process more efficient.
Meeting the Needs of High-Speed Production
High-speed production demands efficiency and consistency. Ultrasonic cutting technology meets these needs by enabling speeds of up to 120 cuts per minute for smaller items like textile labels. For continuous applications, such as long strips of fabric, speeds can reach up to 25 metres per minute.
Using ultrasonic cutting for high-speed production of accessories like belts and straps ensures quick turnaround times without compromising on quality. Straps and masks, which require sturdy, precise cuts, benefit greatly. Our production lines can adapt to various materials, maintaining high standards across different products.
The technology also reduces downtime, as the machines require minimal maintenance and adjustments. This boosts overall productivity and ensures that we can meet tight production schedules efficiently and effectively.
Operational Excellence
When it comes to ultrasonic textile cutting, achieving operational excellence is crucial. Key aspects include maintaining and ensuring the durability of cutting equipment, as well as optimising the cutting process for efficiency and quality.
Maintenance and Durability of Cutting Equipment
Making sure our cutting equipment is well-maintained is essential for operational excellence. Regular checks and service intervals help prevent any unexpected equipment failures, which can halt production. By following a maintenance schedule, we reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of our machines.
Key Maintenance Steps:
- Daily Inspections: Check for wear and tear on blades and other components.
- Routine Servicing: Perform in-depth maintenance at specified intervals to keep equipment in peak condition.
- Component Replacement: Replace worn parts promptly to prevent machine breakdowns.
Proper maintenance ensures that our cutting and welding operations proceed smoothly, enhancing the overall durability and performance of our equipment.
Optimisation of the Cutting Process
Optimising the cutting process involves fine-tuning various parameters to improve efficiency and quality. We analyse factors such as speed, pressure, and frequency to get the best possible results. This process not only improves product quality but also increases productivity.
Optimisation Strategies:
- Speed Adjustments: Setting the optimal cutting speed to balance precision and productivity.
- Pressure Tuning: Adjusting pressure to ensure clean cuts without damaging the material.
- Frequency Calibration: Fine-tuning the ultrasonic frequency for different textiles to achieve seamless cuts.
By focusing on these areas, we make our cutting process more effective, ensuring that we meet both productivity and quality goals across various applications, from technical clothing to non-woven products like nappies and towels.
Frequently Asked Questions
We address some common queries about ultrasonic textile cutting technology, ranging from how it works to its benefits and required maintenance.
How does an ultrasonic textile cutter function?
An ultrasonic textile cutter operates by transmitting vibrations from a horn to the material. This creates frictional heat, which fuses the fabric edges and allows for precise cutting without fraying. The blade of the cutter pulses at a high frequency, usually between 20,000 – 40,000 vibrations per second. This makes the process not only efficient but also clean.
What are the cost implications for implementing ultrasonic textile cutting technology?
While the initial investment in ultrasonic cutting equipment can be high, the long-term cost savings are significant. This is due to reduced wastage, elimination of consumables, and lower maintenance costs. The increased productivity and quality of cuts can also lead to financial benefits over time.
What materials can be effectively cut using ultrasonic technology?
Ultrasonic technology is versatile and can effectively cut a range of materials including textiles, non-wovens, technical fabrics, and even some plastics. This method is especially beneficial for cutting complex or delicate materials, ensuring smooth edges and preventing fraying.
Could you explain the advantages of using ultrasonic cutting over traditional methods?
Ultrasonic cutting offers several advantages over traditional methods. It ensures high precision, clean cuts, and sealed edges, which prevent fraying. The process is faster, reducing production time significantly. Additionally, there is no need for consumables like blades, lowering the operational costs.
What maintenance is required for ultrasonic textile cutting machinery?
Regular maintenance for ultrasonic textile cutting machinery includes checking and cleaning the horn and blade, ensuring all parts are securely fastened, and inspecting for any wear and tear. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to keep the equipment in good working condition.
How does the frequency of an ultrasonic blade affect its cutting efficiency?
The frequency of an ultrasonic blade directly impacts its efficiency. Higher frequencies, like 70 kHz and 35kHz, provide finer, more precise cuts and are suitable for delicate materials. Lower frequencies, around 20 kHz, are better for thicker, tougher textiles. Choosing the appropriate frequency helps achieve optimal cutting performance.
Trouble Cutting Textiles? Send your textile samples to Sabre Plastics Tooling and we can trial ultrasonic cutting the material FOC.
