Ultrasonic welding technology is a fascinating process that utilises high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to create strong joints between similar or dissimilar materials. It has found its place in various industries due to its remarkable speed and efficiency, making it an attractive option for manufacturers.
One major advantage of ultrasonic welding is its speed. The process is exceptionally fast, allowing materials to heat, weld, and cool very quickly. This can significantly reduce production times and costs, making it a valuable method in the fast-paced world of manufacturing.
The process isn’t without its challenges. Ultrasonic welding is typically limited to smaller parts because the pieces being joined must fit together snugly.
Additionally, there are materials and applications where this method may not be suitable, limiting its versatility. Despite these challenges, the advantages it offers, such as strong, clean welds, often outweigh the limitations for many applications.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasonic welding offers fast and efficient production.
- It’s best suited for smaller parts with tight-fitting pieces.
- There are specific applications where ultrasonic welding excels.
Understanding Ultrasonic Welding
The ultrasonic welding process is a precise technique used to bond materials, primarily plastics and metals, through high-frequency vibrations and pressure. This process utilises specialised equipment to efficiently and safely create strong joints.
Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding is a welding technique that involves using high-frequency sound waves to create heat and join materials.
The process starts with converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations using a transducer.
These vibrations, typically in the ultrasonic frequency range of 20 to 40 kHz, are then applied to the materials.
The vibrations generate frictional heat at the interface of the materials, causing them to melt and fuse together. This method is particularly effective for thermoplastics and certain metals.
The process is fast, usually completing in seconds, and requires no additional adhesives or soldering materials, making it cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
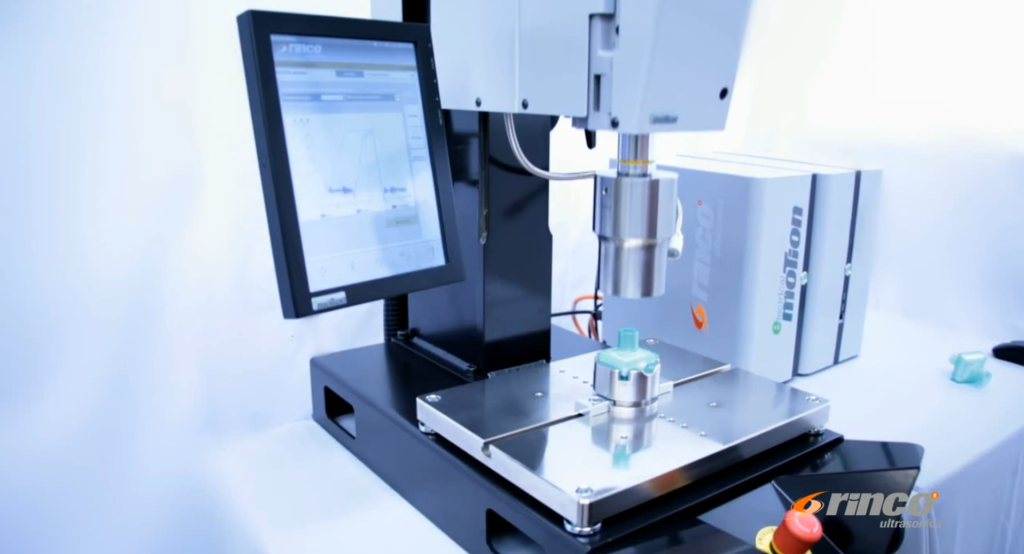

Components of Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
Ultrasonic welding equipment consists of several key components.
The transducer / converter converts electrical energy into ultrasonic vibrations. This energy is then amplified using a booster and transferred through the sonotrode / horn , which directs the ultrasonic energy into the materials to be welded.
The welding equipment also includes an anvil or fixture that holds the materials in place during welding.
The converter is crucial as it ensures the proper ultrasonic frequency and energy are delivered to the materials.
The horn needs to be tuned to the correct frequency for it to run effectively. Poor design of a sonotrode can lead to stress and fatigue of the material causing cracks.
The accuracy of these components is vital for creating strong and reliable welds. Proper alignment and pressure are essential for the efficiency of the welding process.
The Welding Process
The welding process begins by placing the materials to be welded between the sonotrode and the anvil.
The sonotrode then applies pressure and transmits ultrasonic energy into the materials.
The high-frequency vibrations cause the materials to heat and melt at their joining surfaces.
This melting is localised, ensuring minimal impact on the rest of the material.
After a predefined welding time, the ultrasonic energy is stopped, and the materials are allowed to cool and solidify, forming a strong bond.
The entire process is controlled precisely to achieve consistent ultrasonic weld results every time.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding offers numerous benefits, particularly in automotive and medical applications. It is especially effective for joining dissimilar materials, allowing for the fusion of different types of materials without the need for additional fasteners or adhesives. This manufacturing technique stands out for its joint quality, efficiency, and economic benefits, making it a preferred choice for bonding plastics and other materials.
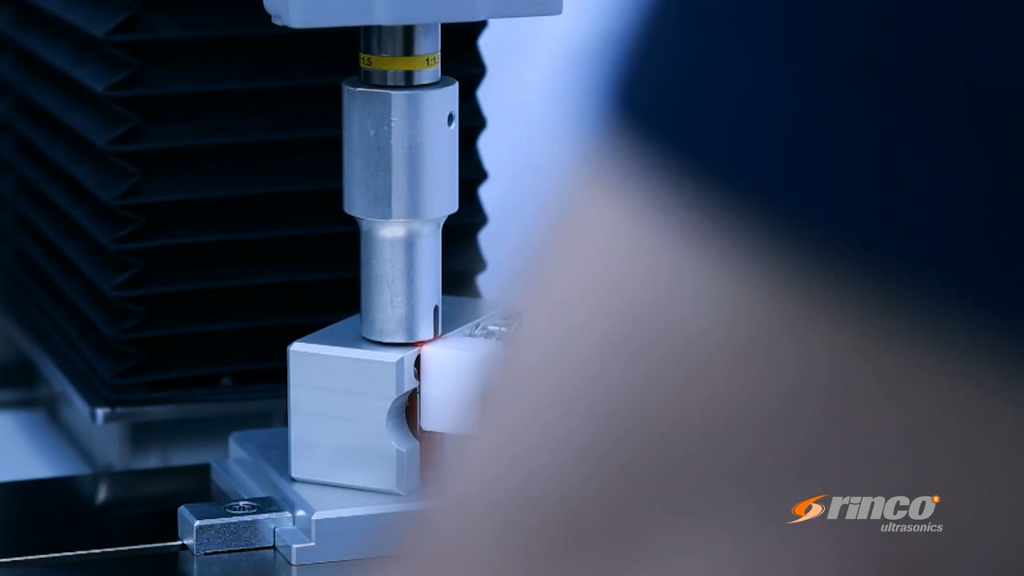
Quality and Durability
Ultrasonic welding creates high-quality joints. The ability to track and control welding parameters is crucial for achieving optimal welding outcomes. The process uses high-frequency vibrations to bond materials, resulting in strong and durable connections.
Because the materials are fused at a molecular level, the joints are incredibly reliable. This is essential in automotive and medical industries, where joint reliability can be critical.
Moreover, ultrasonic welding produces clean joints without the need for adhesives or solvents. This contributes to the overall cleanliness and safety of the process, beneficial in environments that require strict hygiene standards.
Efficiency and Speed
Another significant advantage is the efficiency and speed of the process.
Ultrasonic welding is remarkably fast, often completing bonds in mere seconds. This increases throughput, allowing us to produce more units in a shorter time.
The automated nature of ultrasonic welding also adds to this efficiency.
Machines can be programmed to perform precise, repeatable welds, ensuring consistency across all products.
This is particularly advantageous in large-scale manufacturing environments where consistent quality is crucial.
Additionally, the quick process minimises heat exposure to the materials, reducing the risk of material degradation.
Economic Benefits
Ultrasonic welding is also cost-effective. The lack of consumables like adhesives or solvents reduces material costs.
Lower energy consumption is another economic benefit. The process requires less energy compared to other bonding methods, translating to lower operational costs.
We also benefit from reduced labour costs due to the automated nature of the equipment.
Less manual intervention means fewer workers are needed, further driving down costs.
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding
Let’s examine some specific challenges associated with the ultrasonic welding method, grouped into key categories like material compatibility, equipment expenses, and design constraints.
Material Limitations
Ultrasonic welding works best with materials that have similar melting points. This limits its use to certain plastics and thin metals.
For example, larger or thicker pieces often cannot be welded effectively.
Not all materials are compatible with ultrasonic welding.
Ceramics and glass cannot be welded using this method because they don’t respond well to high-frequency vibrations.
Additionally, composites and some blended materials may not achieve a strong bond.
The need for precise material compatibility can increase the complexity of the welding process, causing difficulties in quality control and consistency. This makes it essential to select materials carefully, which can limit flexibility and increase setup times.
Equipment Costs
Setting up for ultrasonic welding includes significant initial investment.
The equipment is quite specialised, requiring an ultrasonic welder, a generator for converting electrical energy into ultrasonic waves, and a control system. Custom tooling costs can also be substantial.
The purchase price for an industrial ultrasonic welding machine can be high. Maintenance costs also add up over time.
Repairs often require specialist knowledge and parts, which may not be readily available, contributing to additional downtime and expenses.
Lead times for acquiring new machines and setting them up can also extend project timelines.
The sophisticated nature of the equipment necessitates skilled operators, further increasing operational costs.
Design Constraints
Designing parts for ultrasonic welding requires adhering to specific guidelines.
The parts need to fit together precisely and typically must be of a smaller size. This process is generally limited to smaller components, affecting its application in projects involving larger items.
Certain design features, such as complex shapes or uneven surfaces, can be challenging to weld.
The need for exact alignment between parts before welding adds another layer of complexity.
Ultrasonic Welding Applications
Ultrasonic welding is a versatile technique used across various industries. Understanding different welding techniques is crucial for selecting the appropriate method for specific manufacturing needs. This section explores its prominent applications in the automotive, medical, electronics, and aerospace industries.

Applications in the Automotive Industry
Within the automotive industry, ultrasonic welding is crucial for manufacturing parts that require strong, durable bonds.
In particular, we use it for joining instrument panels, electrical components, and interior trim.
The technique ensures fast, clean, and efficient assembly processes. It’s particularly favoured where heat-sensitive materials are involved.
For instance, numerous parts made from thermoplastics can be welded without affecting other vehicle components.
Additionally, the method produces welds that are consistent and precise, reducing the need for post-processing and enhancing overall product quality.
Our goal is to create reliable and safe vehicles, and ultrasonic welding plays a significant part in achieving that.
Applications in the Medical Industry
In the medical industry, ultrasonic welding is indispensable for producing a wide array of medical devices.
We see its use in making filters, catheters, face masks, and other medical garments.
The process ensures a clean and controlled welding environment, crucial for maintaining the sterility of medical products.
One key advantage is the ability to create strong bonds without using adhesives or solvents, which could be harmful or cause allergic reactions.
Moreover, ultrasonic welding is used in attaching flexible tubes to sensors or sheets in diagnostic equipment.
This method ensures that the connections are secure and leak-proof, which is vital for patient safety and the effective functioning of medical devices.
Applications in Electronics and Aerospace
In the electronics and aerospace industries, precision and reliability are paramount.
Ultrasonic welding is used to join delicate components without exposing them to excessive heat.
For example, it’s employed in welding connections in computer parts and creating secure bonds in wire harnesses.
The precision of this technique helps in achieving reliable electrical connections critical for device performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ultrasonic welding offers significant advantages in speed, safety, and material efficiency, though it’s not without limitations. Below, we address common questions about its benefits, applications, and comparisons to traditional methods.
What benefits does ultrasonic welding provide in industrial applications?
Ultrasonic welding is known for its quick process times and minimal need for additional materials like solvents or adhesives. This enhances both safety and environmental sustainability.
It’s particularly efficient for joining thermoplastics and thin metal parts, making it ideal for industries like automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
In what applications is ultrasonic welding considered less suitable?
Ultrasonic welding may not be effective for very thick or hard materials.
It is also less suitable for applications that require highly flexible joints or where the parts to be joined are not made from thermoplastics.
How does ultrasonic welding compare with traditional welding methods?
Compared to traditional welding methods, ultrasonic welding operates at lower temperatures and without added materials like solder.
This often results in faster cycle times and reduced production costs.
Furthermore, the process is generally safer since it involves low levels of heat and energy.
Which materials are typically processed using ultrasonic welding technologies?
Common materials processed with ultrasonic welding include a variety of thermoplastics and certain thin metals.
Plastics like ABS, acrylics, and polycarbonates are frequently welded using this method.
Thin aluminium and copper parts can also be effectively joined using ultrasonic techniques.
What limitations should be considered when employing ultrasonic welding machines?
Despite its advantages, ultrasonic welding has some limitations.
It may not handle very thick materials well and requires precise part alignment for effective bonding.
Moreover, initial equipment costs can be high, and the process may not be suitable for all joint designs.
How does ultrasonic welding impact production efficiency and costs?
Ultrasonic welding can lower overall production costs. It does this by eliminating the need for consumables and reducing cycle times. The process’s efficiency often leads to reduced labour costs and higher throughput. Nonetheless, the initial investment in specialised equipment can be significant. This is a crucial factor to consider.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of ultrasonic welding helps in making informed decisions about its application in various industrial scenarios.
